A Guide on How to Increase Progesterone Levels

Progesterone is a vital hormone in the health of women and people with ovaries. It is crucial in regulating the menstrual cycle, supporting pregnancy, and managing perimenopausal symptoms. Progesterone supports and balances estrogen’s effects. High estrogen levels and lower progesterone levels may lead to a negative set of symptoms, which is why it is easy to understand why we would want to maintain normal progesterone levels.
Problems can occur when progesterone levels are too low or if your hormones are out of balance. For instance, as women age, progesterone levels naturally decline, leading to various health challenges. Given this, you might wonder how to increase progesterone. Fortunately, natural approaches can effectively boost progesterone production and alleviate associated symptoms.
Can You Naturally Increase Progesterone Levels?
Yes, you can enhance progesterone levels naturally and support your body’s hormone production. If you suspect you may be experiencing low progesterone, diet, supplements, and lifestyle changes can help control them.
Understanding the Role of Progesterone and Its Decline in Perimenopause
Progesterone is essential for maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being. It is a vital hormone primarily produced by the ovaries and is often called the “progestational hormone.”
One of its primary functions is to prepare the womb for a potential pregnancy by making it more receptive to a fertilized egg. However, this hormone is not exclusive to pregnancy; its influence extends throughout the menstrual cycle. It helps regulate the menstrual cycle, promotes a sense of calm by acting on the central nervous system, and supports healthy sleep patterns.

During the first half of the cycle, progesterone levels remain relatively low, but there is a slight rise of progesterone before ovulation then the level surge after ovulation. If you don’t conceive during your cycle, progesterone still reaches its peak but decreases towards the end of your cycle to indicate that menstruation is approaching. In anovulatory cycles where ovulation doesn’t occur, you may not observe this peak and decline in progesterone, potentially leading to a missed menstrual period.
Perimenopause is a transitional phase that women typically experience in their mid-40s, leading up to menopause, and it is around the time when your ovaries gradually stop working. So, the ovaries gradually produce less progesterone, leading to hormonal imbalances and various symptoms.
The decline in progesterone during perimenopause disturbs the hormonal balance with estrogen, leading to a range of symptoms. Understanding why progesterone is crucial for their health is beneficial for many women.
Why Progesterone Is Crucial for Women’s Health
Progesterone is crucial for various physiological processes beyond reproduction. It helps regulate mood, supports thyroid function, maintains bone density, and is involved in the body’s response to stress. It is responsible for:
- Menstrual cycle regulation: It prepares the uterine lining for potential pregnancy.
- Pregnancy maintenance: It supports the development of the placenta and helps maintain a healthy pregnancy.
- Perimenopausal symptom management: It helps alleviate hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and other common symptoms.
It is essential to track your progesterone levels as it can help confirm ovulation and make your fertility journey easier. This can help you get pregnant faster and identify ovulation even if LH surges seem low. Tracking progesterone levels can also help you take control of irregular cycles and determine your fertile or infertile window. Additionally, monitoring your hormone levels after getting off birth control can provide valuable information. How can you check your progesterone levels?
There are different ways to monitor progesterone:
- Blood Tests: In this serum progesterone test, a healthcare provider pricks the woman’s finger to retrieve a blood sample to test its progesterone content.
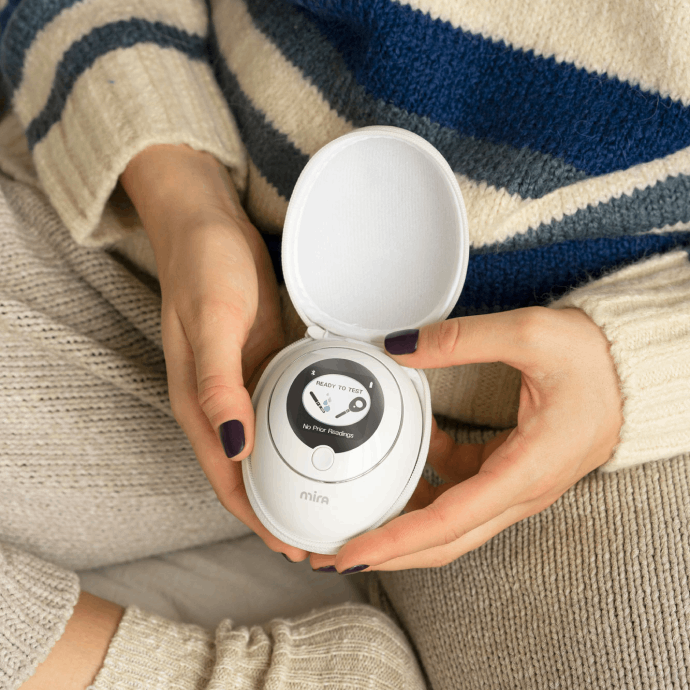
- At-Home Testing: Home tests can monitor the progesterone level through urine samples. These tests estimate that pregnanediol glucuronide (PdG) is a metabolite of progesterone found in urine. These tests can tell if ovulation has happened because rising levels for several days of PdG show high levels of progesterone. For example, the Mira Hormone Monitor can monitor your urine hormone levels. It can help you identify any irregularities in your PdG levels.
Disclaimer: Mira tracks PdG. All the information provided in this article about Progesterone is purely educational. Please always refer to your healthcare provider. - Monitoring Symptoms and Cycle Tracking Apps: Other forms of approximation to progesterone values include timely recording of menstruation cycles and symptoms encountered while in the luteal phase and using fertility apps. Neither of these methods gives precise quantitative results, but they can be used to identify patterns.
- Using Fertility Monitors: Some fertility monitors track hormone levels, such as progesterone, and offer a guide on the menstrual cycle. This makes them convenient for determining the fertility window and even confirming the arrival of ovulation more than common blood testing.
The issue of how to increase progesterone to get pregnant is complex and requires a personalized approach guided by a healthcare professional. Strategies to increase progesterone to get pregnant include eating progesterone-friendly foods, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding too much exercise, and reducing stress. If your progesterone levels are low enough for medical attention, your doctor can prescribe progesterone supplementation or other hormone therapy.

A little extra support from an expert can go a long way
Book an online consultation with one of our Hormone Health Coaches.
Schedule NowCan Diet and Lifestyle Affect Progesterone Levels?
Yes! Your dietary choices and lifestyle habits can significantly impact natural progesterone production. For instance, a balanced diet with adequate nutrients—such as zinc, magnesium, and vitamins B and C—may support healthy hormone levels.
However, processed foods and excess alcohol can create hormonal imbalances. High stress can lead to increased cortisol, which may inhibit progesterone production. Additionally, weight fluctuations can disrupt hormonal balance, affecting progesterone and estrogen levels overall.
Symptoms of Low Progesterone
Low progesterone levels can significantly impact various aspects of health, leading to a range of symptoms that can affect fertility, emotional well-being, and physical health. Here’s a deeper look into the manifestations of low progesterone:
Fertility and Thyroid Issues
Low progesterone often plays a crucial role in fertility. Women with low levels may experience:
- Difficulty Conceiving: Progesterone is vital for preparing the uterine lining for implantation. Insufficient levels can make it challenging to conceive.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Hormonal imbalances can cause cycles to become unpredictable, making it harder to track ovulation and fertility windows.
- Thyroid Imbalances: Progesterone interacts with thyroid hormones; thyroid hormones can affect ovulation and consequently progesterone production, causing energy levels and metabolism to suffer.
- Recurrent Miscarriages: Low progesterone may lead to difficulties maintaining pregnancy, increasing the risk of miscarriage, particularly in the early trimesters.
Estrogen Dominance and Hormonal Imbalances
When progesterone levels drop, estrogen can dominate, resulting in several symptoms, including:
- Heavy Bleeding: An imbalance can lead to heavier menstrual flow, making periods more physically taxing.
- Breast Tenderness: High estrogen levels can cause breast tissue swelling, leading to soreness and discomfort.
- Weight Gain: Women may find it harder to maintain a healthy weight with an estrogen imbalance, as high estrogen can promote fat retention.
- Endometriosis: An imbalance of estrogen and progesterone may worsen the symptoms of endometriosis.
- Fibroids: These noncancerous growths in or on the uterus can thrive in an estrogen-rich environment, which low progesterone can contribute to.
Emotional Symptoms: Mood Swings, Depression, and Anxiety
The fluctuations in progesterone can also lead to emotional distress. Symptoms may include:
- Mood Swings: Hormonal changes can create unpredictable emotional shifts, making one irritable or overly emotional.
- Depression: Low progesterone levels can affect serotonin production, leading to feelings of sadness or hopelessness.
- Anxiety: Hormonal imbalances may heighten anxiety levels, making it difficult to manage stress or maintain a sense of calm.
Physical Symptoms: Weight Gain, Fluid Retention, and Hot Flashes
Women experiencing low progesterone may also face various physical symptoms:
- Weight Gain: The hormonal change may lead to obesity, especially in the belly area.
- Fluid Retention: These receptors may also fluctuate at certain times in a woman’s cycle, and the body can retain more water, resulting in swelling.
- Hot Flashes: Some women state that they get hot flashes or sweating like hot flashes associated with menopause as a result of hormonal changes.
Foods That Increase Progesterone Levels
How to naturally increase progesterone with food depends on what you consume. While progesterone cannot be found in food, a diet high in specific minerals and nutrients can assist your body in producing an adequate and ideal level of progesterone. So, nourishing your body with the right foods can support progesterone production and help maintain hormonal balance.
Key Nutrients for Progesterone Production
Several essential nutrients are crucial for the production and regulation of progesterone:
- Healthy fats: Healthy fats found in avocados, tofu, legumes, fish, nuts, and seeds have been shown to have a hormonal balancing effect. These fats are needed to produce steroid hormones, including the progesterone women.
- Cruciferous vegetables: Green-top vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and kale are among cruciferous crops with compounds that assist with hormones. These vegetables help cleanse the body of excess estrogen, thereby allowing the body to produce progesterone at optimal levels.
- Magnesium and zinc: Women who take magnesium experience the toll stress takes on their bodies, which is vital in maintaining progesterone levels. Zinc also plays an important role in progesterone synthesis; these nutrients are essential for hormonal health.
- Vitamin B6: Closely related to the synthesis of progesterone. Vitamin B6 may also help regulate hormones and the reproductive system.
Magnesium and Zinc-Rich Foods
To boost magnesium and zinc, incorporate the following foods into your diet:
- Dark Leafy Greens: When it comes to magnesium’s rich sources, spinach, Swiss chard, and Kale are at the top of the list.
- Whole Grains: Magnesium and zinc-rich foods include brown rice, quinoa, and oats.
- Legumes: All three, beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are rich sources of these minerals.
- Nuts and Seeds: Magnesium-rich foods include almonds, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds, among others; zinc-rich foods include almonds, among others.
Vitamin B6 and Vitamin C Rich Foods
Vitamin B6 is crucial for fetal brain development and reduces morning sickness; Vitamin C helps build the placenta and the baby’s immune system. Therefore, when pregnant, a woman should ensure that she has foods that have vitamin B6 and vitamin C. Foods rich in vitamin B6 and vitamin C can further enhance progesterone levels:
- Bananas are a convenient source of vitamin B6 and are also healthy to consume.
- Avocados: Aid in formulating hormones while giving the organism healthy fats and vitamin B6.
- Spinach: Packed with vitamin B6, it can be counted in the diet’s list of known nutrient-containing products.
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges contain vitamin C, which aids in the breakdown of progesterone by balancing the hormonal levels in the body. The same applies to lemons and grapefruits.
Many pregnant women who want to get or maintain good bowel movements must take foods that are rich in Vitamin B6 and Vitamin C.
Healthy Fats and Cruciferous Vegetables
Including fats and cruciferous vegetables in any food you eat is crucial to maintaining hormonal balance. Seek to incorporate several foods into your diet to ensure that you get the compounds needed for the synthesis of progesterone.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Factors That Boost Progesterone
Lifestyle modifications can significantly impact progesterone levels and overall hormonal balance. Tips on how to increase progesterone naturally through lifestyle changes include:
- Stress management
- Regular physical activity
- Sufficient sleep
- Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise
- Avoiding xenoestrogens
Stress Management and Relaxation Techniques
Increased stress levels can also lead to improper food that affects the orderly discharge of hormones, resulting in a low level of progesterone hormone. Implementing stress-reduction techniques can be beneficial:
- Yoga and Meditation: These practices will help you better manage stress and unwind.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Regular basics like breathing exercises help reduce stress and actually improve mental health instantly.
The Role of Regular Exercise
Understanding how to raise progesterone through exercise is essential because progesterone is more sensitive to body stress than estrogen. Regular moderate exercise ensures that you are not overweight and increases progesterone levels.
Workout guide based on your menstrual cycle and elevating progesterone levels:
- Days 1-14 (Menstruation to Ovulation): Your energy levels are up, and estrogen has positive effects, so push your limits during high-intensity workouts. Some recommended bodily exercises include HIIT, cycling, running, weight lifting, CrossFit, or swimming.
- Days 15-28 (Post-Ovulation to Menstruation): Your training frequency should also be reduced towards the end of your cycle, although your workouts will still be intense. Avoid activities that cause pressure on the joints; try yoga, walking, swimming, and lifting light weights.
Importance of Consistency in Maintaining Progesterone Levels
In fact, the ability to have good, healthy routines is imperative in leading a hormone-balanced life. For example, appropriate and sufficient exercise, proper diet, and adequate stress management measures, such as appropriate exercise and adequate proportions of foods and vitamins, all help regulate hormone balance in the body, including progesterone.
A hormone health clinic offers one-on-one management services for women in the sexual, reproductive, and post-reproductive stages of their lives. Its prime focus is on treating hormonal disorders and reproductive health. You don’t have to go through your fertility journey blindly, at the Mira Hormone Health Clinic for Fertility, the coaches will create integrative and actionable plans based on your hormone levels that support your fertility and health. With their guidance, you will boost your fertility, balance your hormones, and get pregnant faster.
Supplements and Herbal Remedies to Increase Progesterone Naturally
Some supplements and herbs help increase progesterone levels, although a good diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep also contribute.
Key Supplements: Chasteberry, Vitamin E, and Magnesium
Several key progesterone supplements may help in supporting its production:
- Chasteberry (Vitex): Considered to improve hormonal balance and increase levels of progesterone due to ovulation regulation.
- Vitamin E: It could also help prevent progesterone fluctuations, which is especially important for women’s reproductive systems.
- Magnesium: A macromineral known to have a critical function in the biosynthesis and regulation of hormones.
Mira Prenatal Multi-Vitamins contain Magnesium, Vitamin E, and many other essential nutrients.
These ingredients promote reproductive wellness, and hormonal balance, and boost your fertility health through every stage.
Herbal and Nutritional Support: Vitamin B6, L-Arginine, and Vitamin C
In addition to specific supplements, the following nutrients can contribute to optimal progesterone production:
- Vitamin B6: Favors the building of hormones and maintains balance.
- L-Arginine: An amino acid that enhances blood flow and may improve ovarian function.
- Vitamin C: Plays a role in hormonal regulation and may have a positive effect on progesterone.
Mira’s premium Fertility Tea contains only selected and quality ingredients to enhance fertility wellness by rebalancing hormones and cycles.
Are There Risks and Side Effects of Using Progesterone?
Natural remedies may have less dangerous side effects than synthetic hormones. There are likely risks and complications related to progesterone, whether administered to treat hormonal imbalance or supplements. Anyone thinking of using progesterone should first talk with their doctor before engaging. Here are some of the possible risks and side effects:
- Hormonal imbalance
- Weight changes
- Mood changes
- Headaches
- Breast tenderness
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Menstrual changes
- Potential allergies or reactions
Conclusion
Adopting a holistic approach that includes dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and natural progesterone supplements can effectively support hormone levels and improve overall well-being.
Mira’s Editorial Process
All content produced by Mira meets stringent editorial standards, ensuring excellence and accuracy in language and medical precision. Every piece undergoes thorough fact-checking and review by qualified professionals. Check out our full editorial process to learn more.